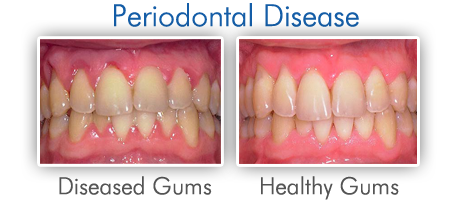
Healthy gums have a pink color and do not bleed. Note that when the dentist describes gum usually is talking about the red tissue surrounding the teeth, and also means various structures responsible for supporting and fixing each tooth in the mouth. There may be an infection or inflammation in the gum at any stage of life, is called receding gums periodontal disease. Even this can happen in a single tooth or more teeth at the same time.
Causes of receding gums periodontal disease

Receding gums periodontal disease corresponds to condition and inflammation of the tissues that support the teeth; the best known: gingivitis and periodontitis. The precipitating cause of receding gums periodontal disease is bacterial plaque that accumulated in the vicinity of the teeth and gums. However, other factors may contribute to or modify the course of this disease, such as diabetes.
Gingivitis is an infection of the gingival, characterized by redness, swelling and bleeding. It is the early stage of periodontal disease, being restricted to the soft tissues, without bone involvement; being reversed with professional help and improvement in personal hygiene.
Periodontitis – When left untreated, gingivitis becomes an infection that affects the supporting tissues of teeth, including bone. As inflammatoryresponse, our body begins to absorb bone condition known as periodontitis. The progress of periodontitis makes teeth change position, be soft or even be lost. To control this disease, the correct professional treatment is required, coupled with good personal hygiene and periodic maintenance to the expert.
Receding gums periodontal disease and general health relationship
Bacteria from an infection can reach the bloodstream to other organs. Studies indicate, in adults, the relationship between periodontal disease and diabetes, heart problems, respiratory problems and problems during pregnancy.
What may favor an increased risk of the emergence of periodontal disease in childhood?
-
Poor oral hygiene;
-
Appearance phase of the teeth in the mouth (dental eruption);
-
Position of the teeth in the mouth, such as crooked teeth;
-
Tooth brushing too hard or wrong moves;
-
Use of orthopedic devices the orthodontic;
-
Hormonal, immunological or systemic changes;
-
Use of certain medications,e.g.,anticonvulsants;
-
Family history;
-
Harmful habits,e.g., thumb sucking;
-
Mouth breathing or the habit of leaving his mouth always open
-
Use of drugs, alcohol or cigarettes.
How to prevent receding gums periodontal disease?
As the triggering factor of receding gumsperiodontal disease is always the plaque attached to the tooth, its prevention is related to localhome care and professional measures. It is emphasized that a prompt diagnosis of receding gums periodontal disease favors the best receding gums treatment outcomes, especially when the disease is associated with systemic changes and heredity.
The best way to promote health is to follow a preventive strategy from early childhood with regular visits to the dentist, with the inclusion of periodontal examination and guidance on oral hygiene to parents and children.
For more natural receding gums treatment tips, visit www.naturessmile.com