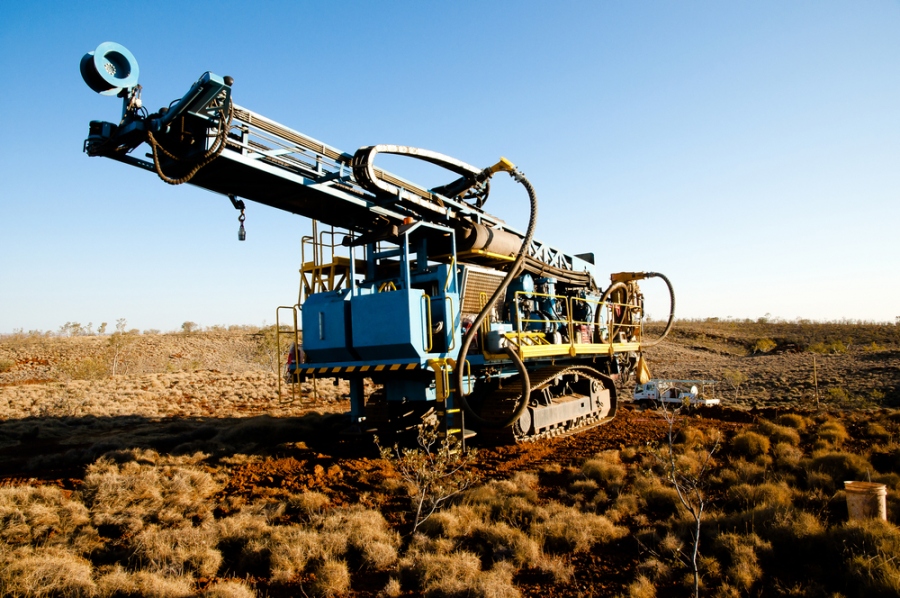
The earth we live in is filled with numerous natural resources in large quantities, but the problem lies in correctly identifying the areas and then extract them. The different types of natural resources that are used for the fulfillment of energy needs include water, natural gas, oil, coal, and various mineral deposits that are used as raw materials in industries.
The earth we live in is mostly covered in water, and nearly 70% of the earth’s surface consists of big oceans, vast seas, and rivers, lakes, and streams. The identification, mapping, and extraction of resources present on the earth’s surface are relatively easy on the land as compared to water surfaces. There are ways to gather the geological information of locations, and one such effective method is through the seismic survey. The survey is a non-invasive and low impact procedure of collecting information that is used to map the structure that lies underneath the ground surface and where minerals might be stored.

The seismic survey is one of the most well-known methods used all over the world for the exploration of petroleum, natural gas, and minerals found in the subterranean structure of the earth. The procedure is not complicated and based on two elements which are
- The time interval that has passed from the initiation of a seismic wave at a selected point.
- The arrival or coming of refracted and reflected impulses by one or more seismic detectors.
The seismic guns are generally used to initiate or generate the seismic waves. The falling weights or electric vibrators are also used to prevent extensive damage where caverns are present. The seismic detectors are used to record the amplitude and timing of the waves to give the information on a seismogram, which also presents the ground vibrations that are studied for a possible earthquake.
The seismic waves are triggered underneath the land surface from one truck while the reflected and refracted waves are received by a receiver vehicle that has instruments called geophones. The study of geology suggests that the density of the rocks increases in depth near to the earth’s surface. The seismic waves initiated near to the ground surface may be received by both reflection and refraction. When the trigger point is close to the receiving point, then the reflected waves are reached first. However, in longer distances, the seismic waves travel faster on the refraction path. The results of the seismic waves are mapped or presented on a cross-sectional drawing of the hidden surface; the drawings are called seismic profiles.
The advancement in technology has given way to 3D (three dimensional) seismic surveys that are low cost and used by nearly all the known companies that explore surfaces of land and sea for natural resources. A seismic wave is triggered by a shock wave, also called the seismic wave, which is sent on a predetermined line by using an energy source. The shock or seismic wave travels to the underneath earth’s surface. It is either reflected or refracted and received or recorded back by geophones that have a similar purpose, such as microphones. A qualified and experienced geophysicist can identify and map the subsurface formations and, by studying the geology of the land, also predict where the gas or oil may be trapped and in how much quantity. The new 3D modeling is based on the old 2D survey, but instead of a single line of energy source and receiver points, multiple sources and receiver points are mapped out on the layout of the land where there is potential oil or gas reserve. The series of reflection and refraction between the energy source and receiver points are recorded from all directions and then analyzed by the computer. The advanced computer with sophisticated software is able to make a 3D image of the subsurface, which makes it easier for exploration and, more importantly, drilling and extraction of oil, gas, or other raw materials.
The best thing about 3D seismic surveys is that they can quickly be conducted on any surface, whether it is land, sea, ocean, or swamp. The 3D seismic survey can cover an extensive area, and the data and information that is collected is valuable and makes it easier for further calculation for exploration. The three aspects of seismic surveys consist of acquiring data, processing data, and then analysis or interpretation of data.
Author Bio:
Susan Clarke is a currently doing majors in geology and also like for online science magazine. She informs readers about the trending science topics and common information that people should know. She recently wrote on Core drilling and how valuable they are in determining the potential site for natural resources.